
Once absorbed, they act on cells like human insulin, but are absorbed from fatty tissue more predictably.
An analog refers to something that is “analogous” or similar to something else. Therefore, “insulin” analogs are analogs that have been designed to mimic the body’s natural pattern of insulin release. These synthetic-made insulins are called analogs of human insulin. However, they have minor structural or amino acid changes that give them special desirable characteristics when injected under the skin. Once absorbed, they act on cells like human insulin, but are absorbed from fatty tissue more predictably.
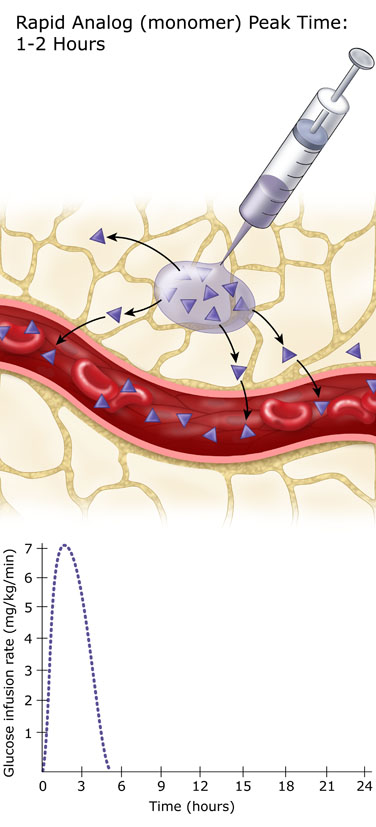
The fastest working insulins are referred to as rapid-acting insulin.
These insulin analogs enter the bloodstream within minutes, so it is important to inject them within 5 to 10 minutes of eating. They have a peak action period of 60-120 minutes, and fade completely after about four hours. Higher doses may last slightly longer, but will last no more than five or six hours. Rapid acting insulin analogs are ideal for bolus insulin replacement. They are given at mealtimes and for high blood sugar correction.
Rapid-acting insulins are used in insulin pumps, also known as continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion (CSII) devices. When delivered through a CSII pump, the rapid-acting insulins provide the basal insulin replacement, as well as the mealtime and high blood sugar correction insulin replacement.
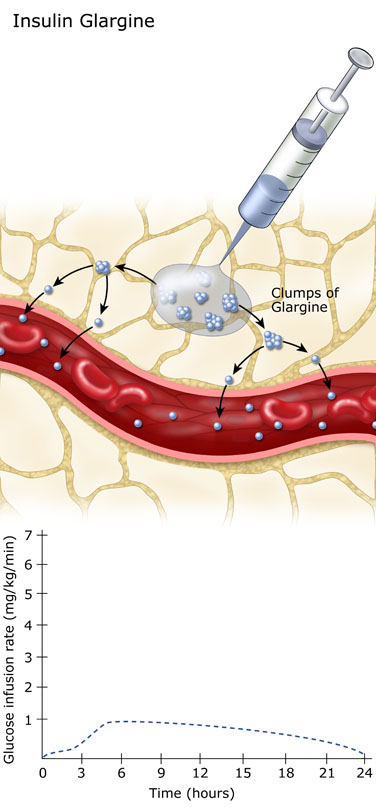
The insulins that work for the longest period of time are referred to as long-acting insulin. They provide relatively constant insulin levels that plateau for many hours after injection. Sometimes these insulins are called “peakless” insulins.
They have an onset of action within 60-90 minutes, maximum effect in around 5 hours that gradually wanes over the next 12-24 hours.
They include:
The long acting insulin analogs are suitable for background or basal insulin replacement. It is important to take insulin detemir and glargine at the same time(s) every day to maintain the most predictable levels of basal insulin.
These long-acting insulins can’t be mixed in the same syringe with other insulins – this could change how the insulin works.
Insulin glargine forms clusters when it is injected under the skin. As the individual insulin units detach from the cluster, the insulin analog can be absorbed into the blood stream. The slow break-up of the insulin cluster gives insulin glargine its long action.
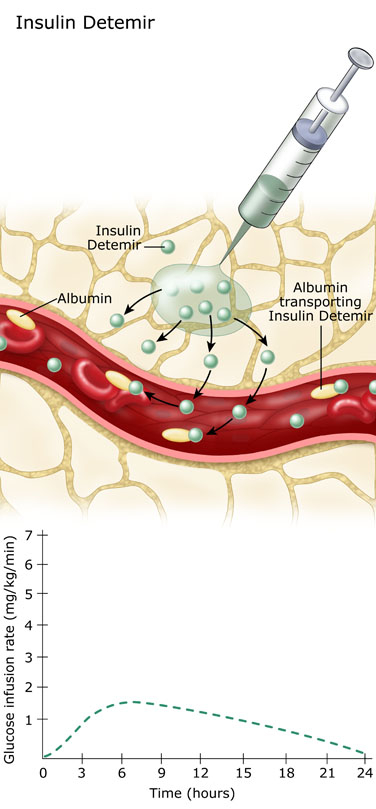
After insulin detemir is absorbed into the blood stream, it becomes attached to a blood protein, albumin. It slowly detaches from the albumin over the next 12-24 hours. The low levels of detached or “free” detemir create the insulin effect.
Self assessment quizzes are available for topics covered in this website. To find out how much you have learned about Treatment of Type 1 Diabetes, take our self assessment quiz when you have completed this section. The quiz is multiple choice. Please choose the single best answer to each question. At the end of the quiz, your score will display. If your score is over 70% correct, you are doing very well. If your score is less than 70%, you can return to this section and review the information.
©2007-2024 Collective work Martha Nolte Kennedy,
The Regents of the University of California.
All rights reserved.